45 how to read a contraction chart
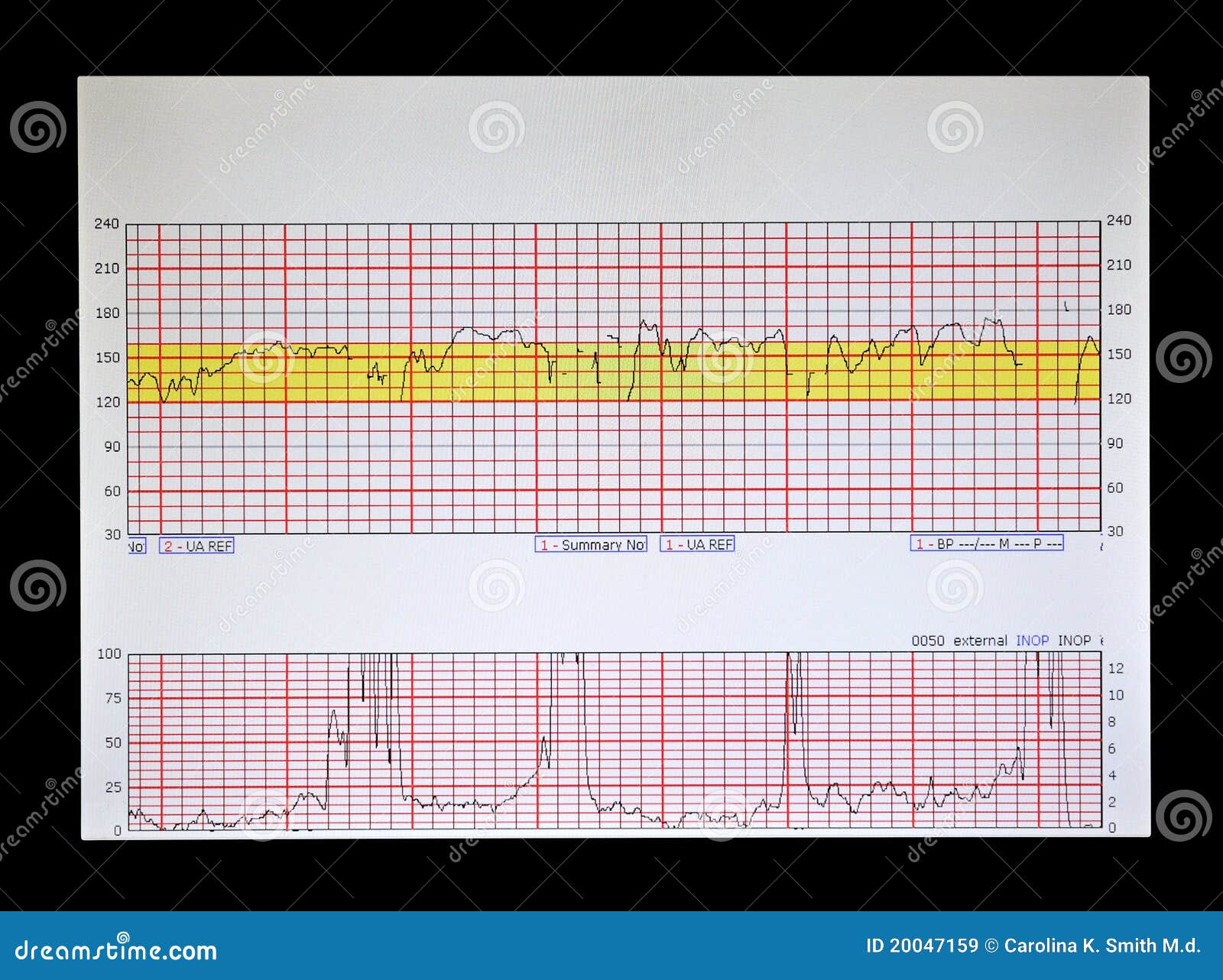
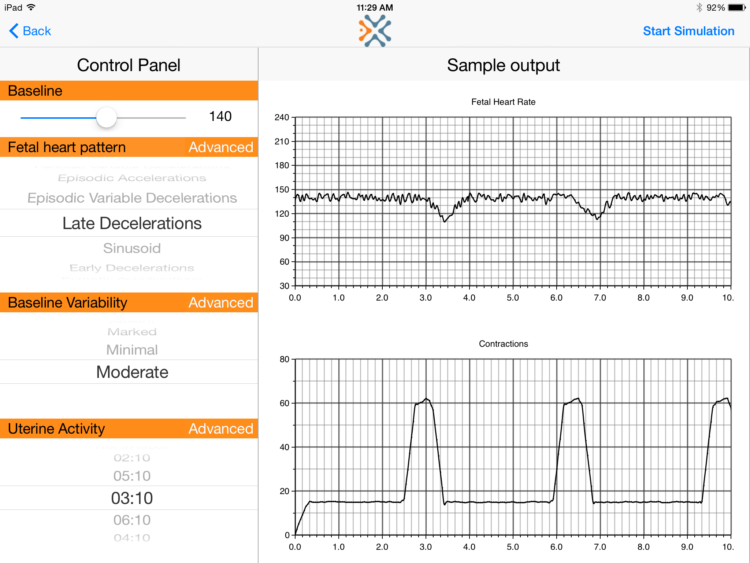
How To Read Toco Monitor? (Here's What You Should Know) How do you count contractions? When timing contractions, start counting from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next. One of the easiest ways to time contraction is to write down the time each contraction starts and ends on a piece of paper, as shown in the following example. A woman is having a contractive period. How to Read a Fetal Monitor During Labor - Verywell Family Electronic fetal monitoring produces a display on a computer monitor or paper graph that records the fetal heart rate and contractions. 5 In the image above, you can see the fetal heart rate marked with the blue indicator. Contractions are in red.
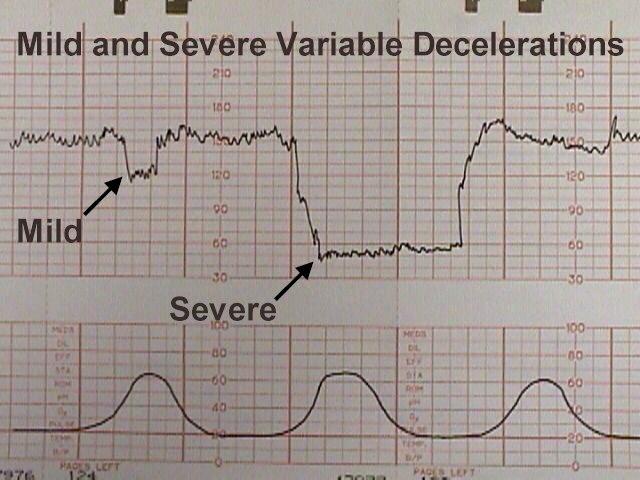
Early, Variable, and Late Decelerations - Registered Nurse RN The baby's heart rate dips slightly at the same time the contraction starts and recovers to a normal range after mom's contraction is over. Early decelerations are nothing to be alarmed about. The reason the baby's heart rate starts to slightly decrease is due to head compression (probably from the baby's head being in the birth canal ...
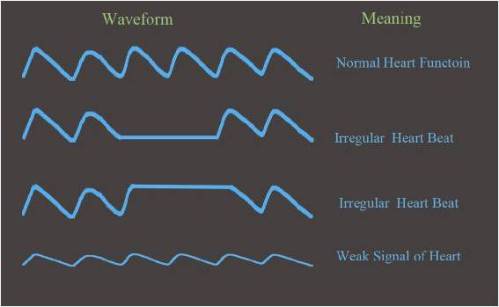
How to read a contraction chart
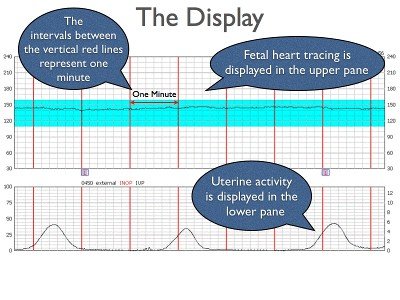
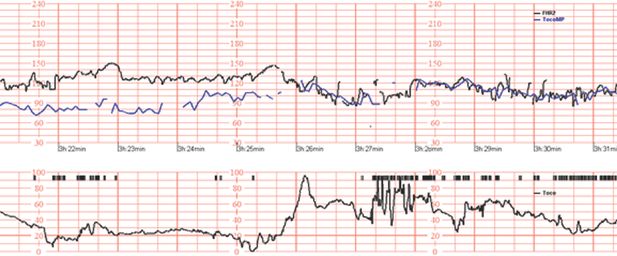
How to Read a Contraction Monitor During Labor - wikihow.com Read it all, below. Things You Should Know An electronic contraction monitor displays 2 charts: 1 depicting your contractions, and another depicting your baby's heart rate. The X-axis on both charts indicates the time in minutes. On your chart, the Y-axis indicates contraction intensity. Blood Pressure Chart: Normal, Elevated, High - Healthline For a normal reading, your blood pressure needs to show: a systolic pressure that's above 90 mm Hg and less than 120 mm Hg, and ; a diastolic pressure that's between 60 mm Hg and less than 80 ... How to Read a Fetal Monitor Strip | Healthfully Find the toco, or uterine contraction tracing, in the bottom half of the strip. The baseline when the woman's abdomen is relaxed will be from zero to 10. The tracing starts to rise when the contraction begins, bell curves to indicate peak tension, and comes back to baseline when the contraction ends.
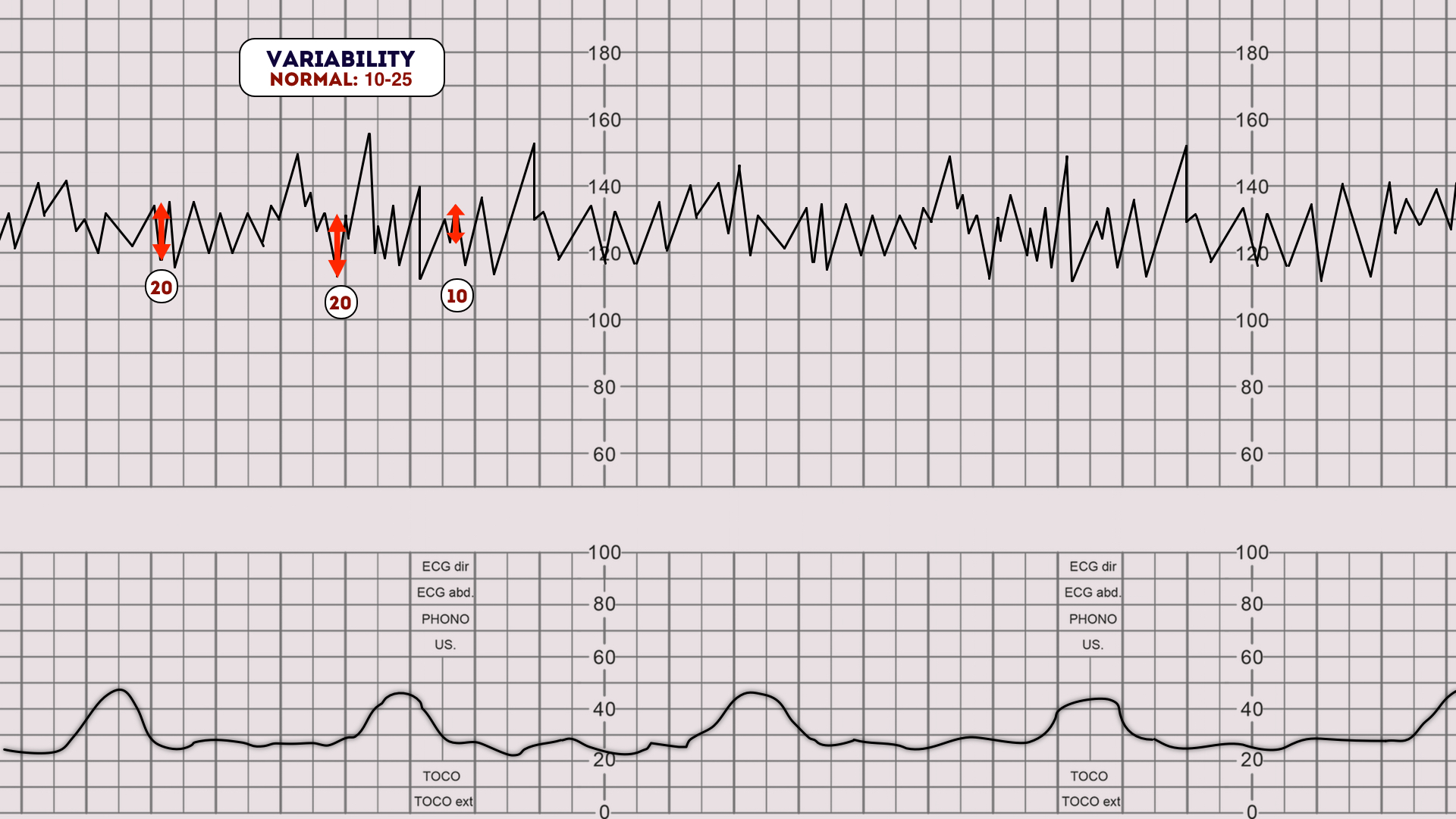
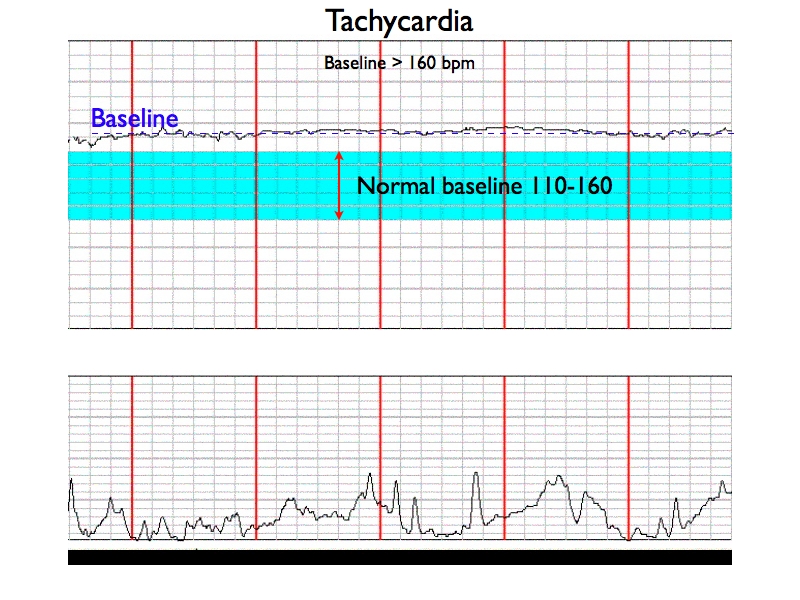
How to read a contraction chart. How to Read a Fetal Monitor Strip | Hello Motherhood Identify the baseline heart rate. Locate the number of beats per minute on the top section of the fetal monitor strip. A range of 120 to 160 beats per minute indicates a normal fetal heart rate but a deviation, or change, of 10 beats or less in your baby's heart rate is normal. How to Read a CTG | CTG Interpretation | Geeky Medics To interpret a CTG you need a structured method of assessing its various characteristics. The most popular structure can be remembered using the acronym DR C BRAVADO: DR: Define risk C: Contractions BRa: Baseline rate V: Variability A: Accelerations D: Decelerations O: Overall impression 20 Contraction ANCHOR CHART ideas | teaching reading ... - Pinterest Contractions anchor chart Classroom Language Teaching Tools Teaching English Grammar Activities This is a flip book that the students could make to help them learn about contractions. It shows the two words and then the contraction that they make. Homeschool Language Arts Teaching Resources Language Resources Learning Tools We're in Love With These 23 Fantastic 2nd Grade Anchor Charts This anchor chart shows a few common examples of contractions and how two words combined make a contraction. 13. Writing Ideas Source: Teaching with Terhune Even second graders can get writers block. If kids have no clue what to write about, show them this chart to get them started on the "write" path. 14. Substitute Teacher Rules
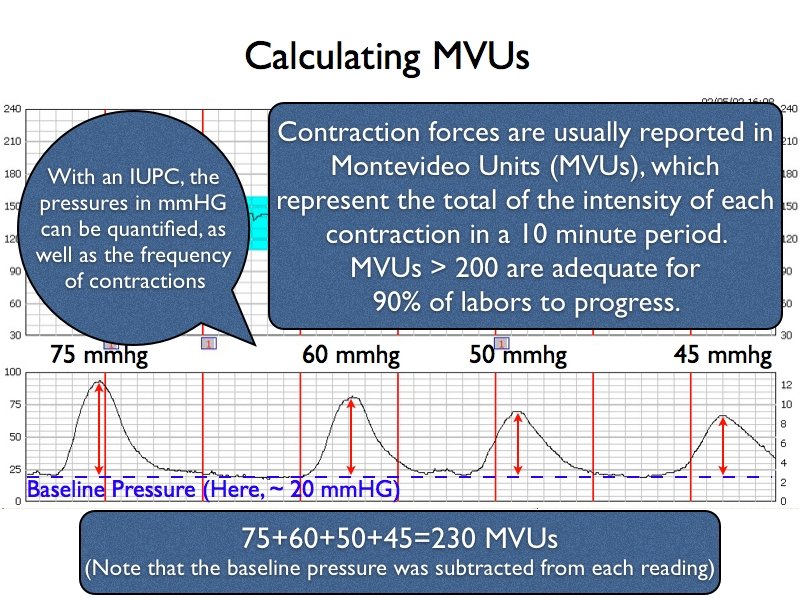
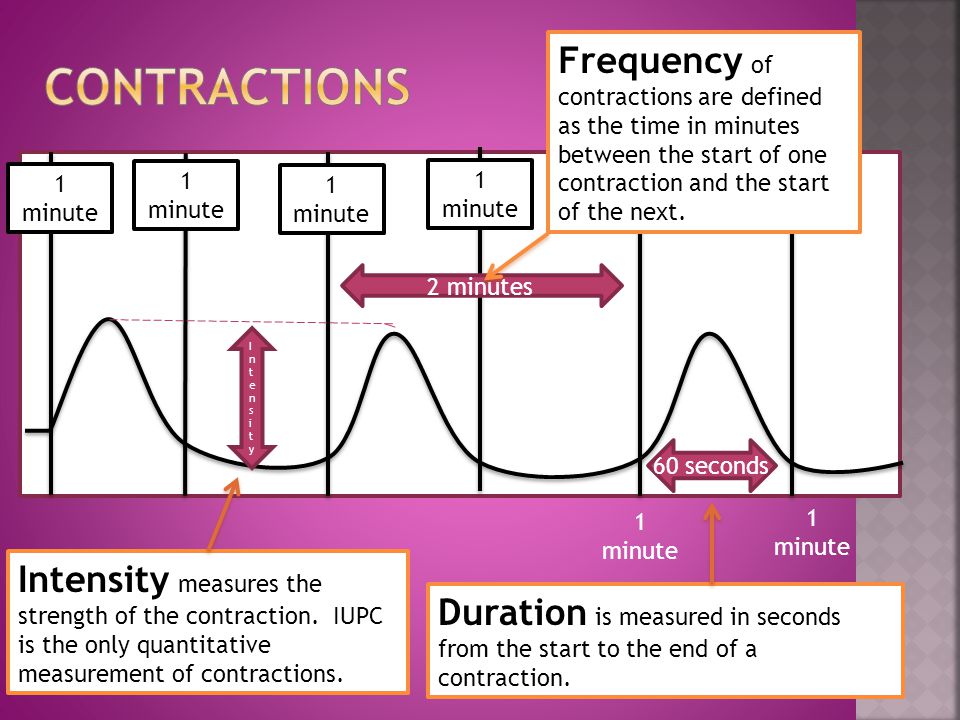
WHO Partograph for Beginner - Contemporary OB/GYN Measured in seconds from the time the contraction is first felt abdominally, to the time the contraction phases off • Each square represents one contraction Palpate number of contraction in ten minutes and duration of each contraction in seconds • Less than 20 seconds: • Between 20 and 40 seconds: • More than 40 seconds Part 111: maternal condition READING AND INTERPRETING A FETAL HEART RATE MONITOR - YouTube In this video I discuss the normal and abnormal variations on a fetal heart rate and related nursing interventions.Follow along and study by answering these ... Contractions "anchor Charts" Teaching Resources | TPT Here are contractions anchor charts that will help your students learn the steps on how to write contractions! Each anchor chart has clear step-by-step directions on how to write the contractions correctly. Hang the anchor charts up on your wall, bulletin board, or in your writing center. These anchor charts are aligned with Science of Reading! How to Read a Contraction Chart - Vigour Youths Network In women in spontaneous labor, more than 40% have UVM > 300 mmHG. The basic pressure or resting tone is the uterine pressure in mm Hg while the uterus is relaxed. The accelerations that occur alongside uterine contractions are a sign of a healthy fetus. Sometimes it is easier to read impressions by looking at them from the side.
Basic Pattern Recognition - Electronic Fetal Monitoring In association with a uterine contraction, a visually apparent, gradual (onset to nadir 30 sec or more) decrease in FHR with return to baseline Nadir of the deceleration occurs at the same time as the peak of the contraction (NICHD) An early deceleration and a late deceleration may visually appear identical. How To Read A Fetal Monitor In Labor - CureJoy On the left-hand side, there is the y axis in each of the graphs. The blue indicator is showing you the marking for the fetal heart rate. These are beats per minute (bpm), measured in increments of ten with markings every 30 beats. On the left at the bottom with the red indicator, you will see the y axis measures millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Interpretation of the Electronic Fetal Heart Rate During Labor Identify pattern of uterine contractions, including regularity, rate, intensity, duration and baseline tone between contractions. 6. Correlate accelerations and decelerations with uterine ... How to Read a Stock Chart - YouTube If you're a new trader, you might not know where to begin. This video will teach you the basics of reading stock charts.TD Ameritrade, Inc. is a subsidiary o...
Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring | AAFP Continuous electronic fetal monitoring is the continuous monitoring of fluctuations of the fetal heart rate (FHR) in relation to maternal contractions and is considered standard practice during...
Understanding Your EMG Results | Nerve Conduction Study ... - Healthgrades An EMG is a nerve conduction study that evaluates a muscle's response to the nerve that controls it. It does this by measuring the electrical activity in the muscle at rest, with a slight contraction, and with a forceful contraction. This helps your doctor know whether the problem is in the muscle itself or in the nerves that control the muscle.
Contractions Anchor Chart Teaching Resources | TPT - TeachersPayTeachers Here are contractions anchor charts that will help your students learn the steps on how to write contractions! Each anchor chart has clear step-by-step directions on how to write the contractions correctly. Hang the anchor charts up on your wall, bulletin board, or in your writing center. These anchor charts are aligned with Science of Reading!
Introduction to Stock Chart Patterns - Investopedia Trendlines are straight lines drawn on a chart by connecting a series of descending peaks (highs) or ascending troughs (lows). A trendline that angles up, or an up trendline, occurs where prices...
Understanding TOCO Monitor (Tocodynamometer): How to Monitor and Read ... One patient may have a baseline reading of 10 mmHg at rest between contractions, and another may have a baseline of 15 mmHg. Baselines provide a foundation from which to interpret the upcoming data. If the patient begins to feel tightenings or contractions, the toco number should rise from the baseline.
Contraction Timer & Calculator For Labor Pains - MomJunction How to use the contraction calculator? • Click the "Start counting" button when you feel a tightening sensation (you can either feel it from inside or with your hand on the belly). This is the beginning of one contraction. • Click the "Stop counting" button when you feel the relaxation of the uterus.
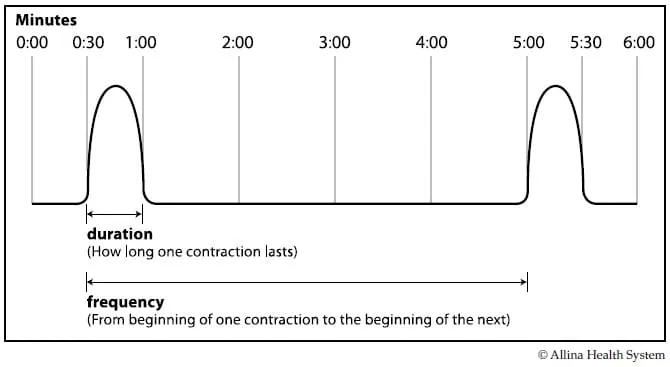
How to Time Contractions | Pampers Here's how to time your contractions: Make a note of the time when your first contraction starts ("time" on the table below) Write down how long the contraction lasts ("duration") Then mark the length of time from the start of the contraction to the start of the next one ("frequency")
Contraction Tracking Chart - Printable Tracking Guide | Pampers A printable contraction tracking chart is such a useful resource to have close to hand when you start labor. Our simple free guide makes it so easy to note the time, duration and frequency of your contractions and allows you or your birth partner to track your progress in a clear and organized way. Diapers Wipes Smart Sleep Coaching
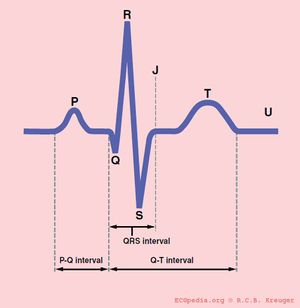
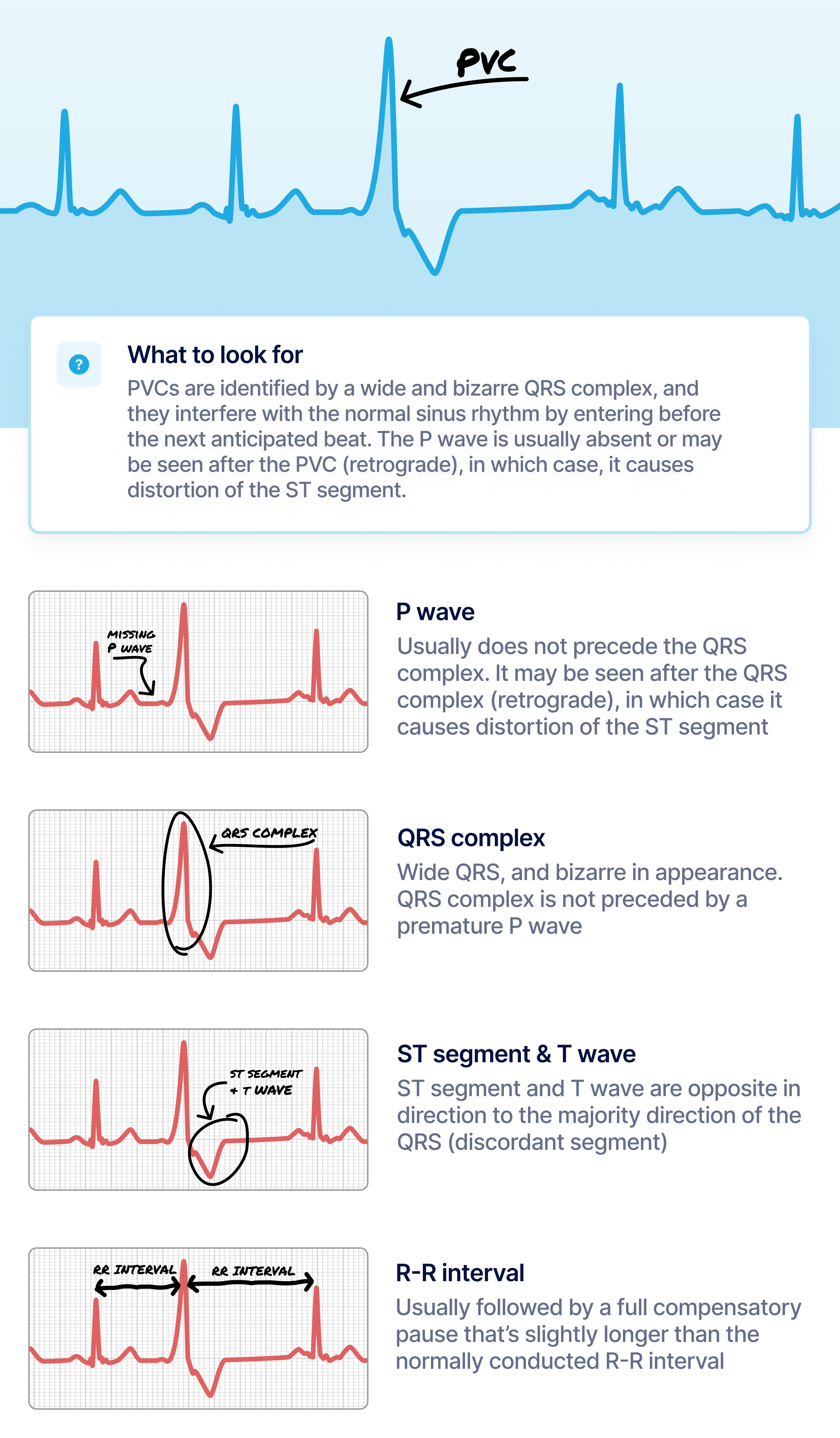
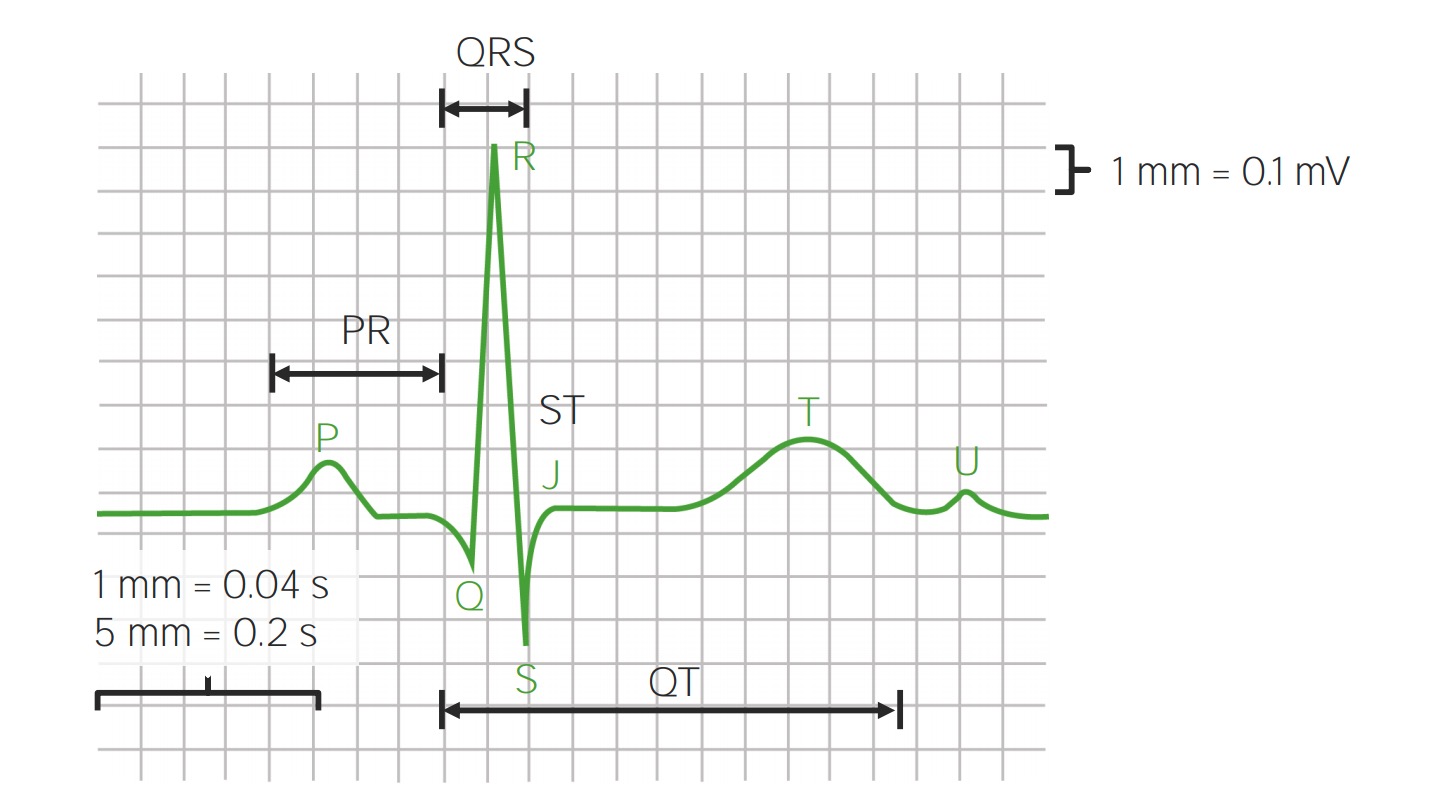
EKG Interpretation & Heart Arrhythmias Cheat Sheet - Nurseslabs Premature Junctional Contraction (PJC) occurs when some regions of the heart becomes excitable than normal. It has the following characteristics. ADVERTISEMENTS PR interval less than 0.12 seconds if P wave precedes QRS complex QRS complex configuration and duration is normal P wave is inverted Atrial and ventricular rhythms irregular
9 Fantastic Contractions Anchor Chart to Use & Inspire Another fun way to envision contractions is to picture the extra letters being kicked out by some tiny karatekas, such as we see in this anchor chart. It includes a few examples of common contractions underneath the illustrations.
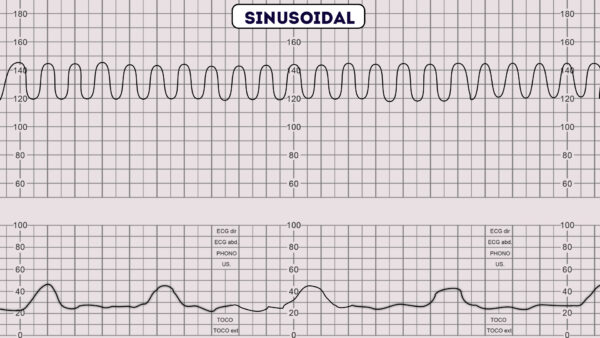
How to Read a Fetal Non-Stress Test (NST) - CardiacDirect Baseline Variability. The first step to reading an NST is to find an average fetal heart rate reading over 10 minutes. For instance, the normal fetal HR is between 110 and 160 BPM. However, because we are monitoring fetal movement, we want the baseline heart rate to change in the long run. Absent: 0 BPM Variation.
How to Read a Fetal Monitor Strip | Healthfully Find the toco, or uterine contraction tracing, in the bottom half of the strip. The baseline when the woman's abdomen is relaxed will be from zero to 10. The tracing starts to rise when the contraction begins, bell curves to indicate peak tension, and comes back to baseline when the contraction ends.
Blood Pressure Chart: Normal, Elevated, High - Healthline For a normal reading, your blood pressure needs to show: a systolic pressure that's above 90 mm Hg and less than 120 mm Hg, and ; a diastolic pressure that's between 60 mm Hg and less than 80 ...
How to Read a Contraction Monitor During Labor - wikihow.com Read it all, below. Things You Should Know An electronic contraction monitor displays 2 charts: 1 depicting your contractions, and another depicting your baby's heart rate. The X-axis on both charts indicates the time in minutes. On your chart, the Y-axis indicates contraction intensity.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-read-a-fetal-monitor-in-labor-2758718-electronic-fetal-monitoring-measures-259e633e776f477f903d321feec665ca.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-177676958-56a772765f9b58b7d0ea9785.jpg)










0 Response to "45 how to read a contraction chart"
Post a Comment